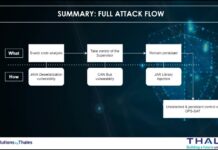
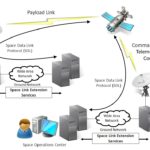
In this article, we will explore if we can apply Zero Trust in space domain, for example in satellites or space missions, how and why ?
What is Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
The Zero Trust security model, coined by analyst firm Forrester Research, is a holistic approach to network security that mandates no user or machine should be implicitly trusted, either outside or inside of the network. The concept has evolved as a way to minimize cyber threats and data breaches by not granting automatic trust based on network location.
Understanding Zero Trust Principle and Architecture:
Zero Trust operates on the concept “Never Trust, Always Verify”. At its core, it’s designed to protect modern digital environments by leveraging network segmentation, preventing lateral movement, providing Layer 7 threat prevention, and including simplified granular user-access control.
In a Zero Trust architecture, security isn’t treated as a one-size-fits-all model. It aims to eliminate uncontrolled access to resources by assuming that a user, system, or device is potentially compromised, regardless of if they are inside or outside of the security perimeter.
Implementing Zero Trust includes but not limited to: Identify Sensitive Data, Micro-segmentation, Multi-factor Authentication (MFA), Real-time Monitoring and Analytics, User Access Control
Application & Scope:
Zero Trust can be applied to any IT environment, from on-premises data centers to public clouds, and from network to endpoints. This approach is highly effective in protecting users and data in today’s perimeter-less workplaces, where employees, contractors, and partners need to access applications from various locations, networks, and devices.
Importance & Future of Zero Trust:
The increasing complexity and fluidity of modern IT environments make traditional perimeter-based security models obsolete. Evolving security threats, remote workforce, digital transformations, cloud adoptions, and complex supply chains led to an increase in the number of digital touch-points that can serve as entry points for sophisticated cyberattacks.
Zero Trust’s focus on securing every access point draws a promising future for IT security. It emphasizes understanding the behavior of network users and devices, thereby enabling early detection and mitigation of potential threats. It offers greater visibility into network activities, lowers the risks of security breaches, and improves compliance by implementing granular data control.
From organizations looking to secure their remote workforces to businesses wanting to lock down their supply chains, Zero Trust is poised to become the new normal for cybersecurity. As entities come to grips with a ‘trust no one’ model, they will be better positioned to tackle the cybersecurity threats of the future.
Does Zero Trust apply to the space domain?
In theory, the Zero Trust model could feasibly be applied to the space domain. The fundamental principles of identity verification, least privilege access and real-time monitoring that define Zero Trust are universally important for any operational technology, including space missions or satellites.
Security in the space domain is critically important. Satellites and other space technology manage a wide range of sensitive data and information, from global positioning data to confidential national security information.
Why Apply Zero Trust in the Space Domain?
Protecting Sensitive Information: Considering the increasing cost and strategic importance of space systems, as well as the sensitivity of the data they handle, implementing a robust security posture like the Zero Trust model is crucial.
Remote Accessibility: Like many other systems in the digital age, space platforms are remotely accessed. Zero Trust principles don’t inherently trust any request for access, making it harder for an unauthorized user or a potential hostile actor to gain control.
Increased Cyber Threats: As technology advances, so does the sophistication of cyber threats. Applying Zero Trust principles can help protect against potential cyberattacks targeting space assets.
Implementing Zero Trust in Space Domain
For implementing Zero Trust in the space domain, we need to consider several elements:
Authentication: Implement stringent verification measures to corroborate the identities of all users and devices that interact with the system.
Encryption: As data travels from Earth to space and back again, it needs to be encrypted to protect against interception.
Monitoring & Analytics: It’s crucial to monitor network behavior and traffic patterns continuously. Anomalies or irregularities can indicate potential threats that require immediate attention.
Limited trust: Only provide access to systems and data that are absolutely necessary for each user or device.
What are the challenges applying Zero Trust in the Space Domain?
An interesting challenge here is the vast distance of space and the latency it imposes on operations. The implementation of Zero Trust will have to consider the time delay for authentications as well as a secure and efficient key exchange mechanism for encryption.
Thus, applying the principles of Zero Trust in the space domain offers an exciting opportunity in providing secure and reliable communications. While it presents its unique challenges, given the importance of assets in the space domain, the need for enhanced security measures is undeniable, and a Zero Trust model may be the best way forward.